CP-template-AND-interesting-problems
Keeping On Track Problem Link
Problem
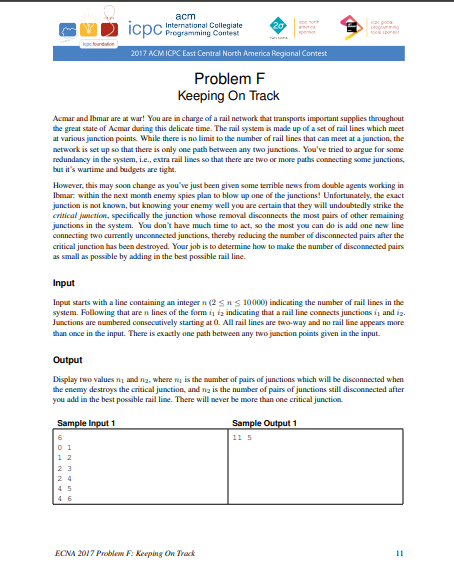
problem simplified:
Given a tree. First we have to find a vertex, such that, if we delete that vertex, number of disconnected pairs will be maximum.
Let, after deleting a vertex, three disconnected component of size s1, s2, s3 is
created. then disconnected pairs = s1*s2 + s1*s3 + s2*s3
Secondly, we have to put an edge between any two vertex to minimize the number of disconnected pairs.
So, we have to find maximum disconnected pairs of vertex we can have have initially, and maximum disconnected pairs of vertex after putting an edge(this edge minimize the number of pairs).
Solution Idea
- First we will calculate all the disconnected component for each node. We ca easily do this with a single
dfs.(in the code we have saved our disconnected component in thersvector) - Then we iterate over all the vertex and count disconnected pairs for each of them, and maximum of which is our 1st answer.
- Then for that node, we will connect 2 disconnected components of max size, and again calculate the disconnected pairs. This will be our 2nd answer.
Solution Code(C++)
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int n;
vector<int>graph[100000];
vector<int>rs[100000];
int dfs(int s,int p){
int sm = 0;
for(int i=0; i<graph[s].size(); i++){
int v = graph[s][i];
if(v != p){
int sz = 1+dfs(v,s);
rs[s].push_back(sz);
sm += sz;
}
}
if(n-sm) rs[s].push_back(n-sm);
return sm;
}
int main() {
cin>>n;
for(int i=0; i<n; i++){
int u,v; cin>>u>>v;
graph[u].push_back(v);
graph[v].push_back(u);
}
dfs(0,-1);
int ans = 0, idx = 0;
for(int i=0; i<=n; i++){
int mul = 0;
for(int j=0; j<rs[i].size(); j++){
for(int k=j+1; k<rs[i].size(); k++){
mul += (rs[i][j]*rs[i][k]);
}
}
if(mul > ans){
ans = mul;
idx = i;
}
}
sort(rs[idx].begin(),rs[idx].end());
int val = rs[idx][rs[idx].size()-1] + rs[idx][rs[idx].size()-2];
rs[idx].pop_back();rs[idx].pop_back();
rs[idx].push_back(val);
val = 0;
for(int j=0; j<rs[idx].size(); j++){
for(int k=j+1; k<rs[idx].size(); k++){
val += (rs[idx][j]*rs[idx][k]);
}
}
cout<<ans<<" "<<val;
}